Convert iOS app to Android, and also you’re embarking on an interesting journey! Consider it as a quest, an exciting expedition the place your loved one iOS app will get a brand new lease on life, prepared to overcome the huge Android panorama. Why enterprise into this territory? Maybe you are keen to achieve a wider viewers, faucet into the colourful Android market, or just discover the boundless potentialities that lie inside a distinct ecosystem.
The trail forward is paved with thrilling challenges and rewarding discoveries.
This journey includes understanding the technical nuances, from the languages we communicate (Swift/Goal-C vs. Java/Kotlin) to the design philosophies that form our person interfaces. We’ll delve into the varied conversion strategies, from the meticulous artwork of native conversion to the versatile approaches provided by cross-platform frameworks. We’ll additionally navigate the UI/UX design, testing, efficiency optimization, and the ultimate flourish: deployment and distribution.
It is a complete exploration, providing insights for each stage of this transformative course of.
The iOS to Android Conversion Problem: Convert Ios App To Android
Embarking on the journey of changing an iOS app to Android is like translating a posh novel from one language to a different – it requires understanding the nuances of each techniques and a strategic method. It is a course of that, whereas doubtlessly advanced, can unlock vital alternatives for builders.Changing an iOS app to Android includes rewriting the app’s code, or parts of it, to operate on the Android working system.
This typically consists of adapting the person interface (UI) to align with Android’s design pointers, guaranteeing compatibility with totally different Android units, and testing the app completely to establish and repair any bugs or efficiency points. This could vary from an entire rewrite in languages like Java or Kotlin, the native languages for Android growth, to utilizing cross-platform frameworks like React Native or Flutter, which permit code reuse between the 2 platforms.
Causes for iOS to Android Conversion
Builders select to transform their iOS apps to Android for a wide range of compelling causes, typically pushed by the will to broaden their attain and maximize their potential.
- Wider Market Attain: Android boasts a considerably bigger international market share in comparison with iOS. This implies changing to Android offers you entry to a wider viewers, doubtlessly rising downloads, person engagement, and income. Statista experiences that Android’s international market share hovers round 70-75%, whereas iOS accounts for roughly 25-30%. This stark distinction underscores the potential for exponential progress.
- Elevated Income Potential: With a bigger person base comes a larger alternative for monetization. Whether or not by in-app purchases, subscriptions, or promoting, the Android platform affords a considerable avenue for income era. Contemplate the case of a preferred gaming app that’s obtainable on each iOS and Android. If the app’s Android model attracts even a fraction of the market share, the income generated could be vital, straight impacting the developer’s backside line.
- Platform Range: Android’s open-source nature fosters a various ecosystem of units, from budget-friendly smartphones to high-end tablets and wearables. This variety gives builders with alternatives to tailor their apps to particular units and person wants. For instance, a health app could be optimized for smartwatches operating Put on OS (Android’s wearable platform), increasing its utility and attraction.
- Cross-Platform Code Reuse: Using cross-platform frameworks can considerably cut back growth time and value. These frameworks enable builders to jot down code as soon as and deploy it on each iOS and Android, streamlining the conversion course of. Firms like Airbnb and Alibaba have efficiently used cross-platform frameworks, demonstrating the viability of this method for advanced functions.
- Aggressive Benefit: Having an app obtainable on each iOS and Android platforms is not a luxurious, however a necessity. By providing your app on Android, you keep aggressive and cater to the various preferences of your target market. In at this time’s market, customers count on cross-platform availability, and never offering it may well result in missed alternatives.
Variations Between iOS and Android Platforms Impacting Conversion
The basic variations between iOS and Android platforms necessitate cautious consideration throughout the conversion course of. These variations contact upon a number of crucial areas.
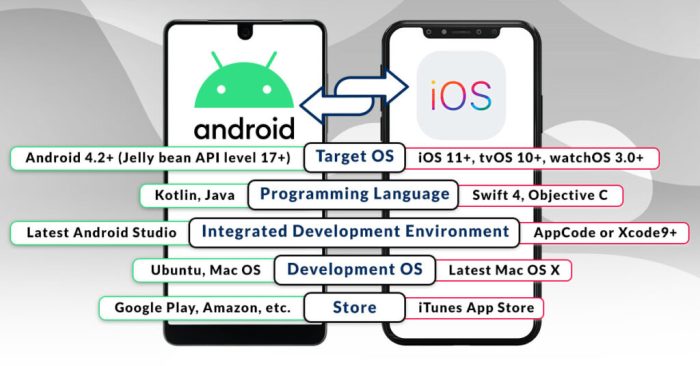
- Programming Languages: iOS apps are primarily developed utilizing Swift or Goal-C, whereas Android apps historically use Java or Kotlin. This implies builders typically have to be taught a brand new language or leverage cross-platform instruments. The transition could be smoother with frameworks like React Native (utilizing JavaScript) or Flutter (utilizing Dart), permitting for code reuse and quicker growth.
- Person Interface (UI) Design: iOS and Android adhere to distinct design philosophies. iOS emphasizes a clear, minimalist design with a deal with simplicity, whereas Android permits for extra customization and suppleness. Builders have to adapt the UI to align with Android’s Materials Design pointers to make sure a constant and user-friendly expertise.
- {Hardware} and Machine Fragmentation: Android’s open-source nature results in a fragmented ecosystem with all kinds of units, display screen sizes, and {hardware} specs. This requires builders to check their apps on a variety of units to make sure compatibility and optimum efficiency. iOS, with its managed {hardware} ecosystem, affords a extra constant expertise.
- Working System Variations: Each platforms launch common updates. Nevertheless, the adoption fee of latest OS variations can differ considerably. Android customers could also be slower to replace their units, requiring builders to help older OS variations to achieve a broader viewers. Apple customers are inclined to replace their units extra rapidly, offering a extra uniform atmosphere.
- Improvement Instruments and Ecosystem: iOS growth depends on Xcode, a complete built-in growth atmosphere (IDE) supplied by Apple. Android growth makes use of Android Studio, which can also be a strong IDE, however with its personal set of instruments and options. Builders have to familiarize themselves with these totally different environments and instruments.
- Testing and Debugging: Testing on Android includes navigating a various vary of units and configurations, requiring thorough testing methods. iOS affords a extra streamlined testing atmosphere. Debugging processes and instruments additionally differ between the 2 platforms.
“The journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step.”
Lao Tzu.
Understanding the Technical Variations
Changing an iOS app to Android is like translating a novel from English to Spanish – the core story stays, however the language, type, and even the cultural nuances require cautious consideration. This course of calls for a deep understanding of the basic technical disparities between the 2 platforms. Ignoring these variations can result in a subpar Android app, riddled with efficiency points, and failing to resonate with the Android person base.
Programming Languages and Their Conversion Implications
The center of any cell app lies in its programming language. iOS apps are primarily written in Swift (the fashionable selection) or Goal-C (the legacy language), whereas Android apps make the most of Java or Kotlin. This distinction presents a big hurdle throughout conversion.Swift and Goal-C are each object-oriented programming languages, however they’ve distinct syntax and options. Swift, recognized for its security and pace, is a extra trendy language, whereas Goal-C, whereas highly effective, is older and could be extra advanced.
Java, initially developed by Solar Microsystems, can also be object-oriented and has been a staple in Android growth. Kotlin, nevertheless, is the fashionable, most well-liked language for Android, providing concise syntax, improved security, and interoperability with Java.Changing code includes greater than only a direct translation. The core logic must be rewritten, and builders should take into account:
- Syntax Variations: Swift and Goal-C use totally different syntax buildings in comparison with Java and Kotlin. For instance, the way in which you declare variables, deal with loops, and handle reminiscence differs.
- API Variations: iOS and Android present totally different APIs for performing the identical duties. Changing code that interacts with these APIs requires discovering equal capabilities and lessons within the goal platform.
- Reminiscence Administration: Swift employs Computerized Reference Counting (ARC), whereas Java makes use of rubbish assortment. Kotlin additionally makes use of rubbish assortment, however builders should perceive how these totally different approaches have an effect on reminiscence utilization and potential efficiency bottlenecks.
- Code Construction: The group of code, using design patterns, and the general structure of the app will probably want changes to align with Android greatest practices.
UI/UX Design Issues for iOS and Android
The person interface and person expertise (UI/UX) are crucial for an app’s success. Whereas each iOS and Android intention to supply a seamless expertise, they’ve distinct design pointers and conventions. Ignoring these variations can result in an app that feels misplaced and fails to have interaction Android customers.Apple’s iOS emphasizes a clear, minimalist design with a deal with simplicity and ease of use.
Android, alternatively, embraces a extra versatile and customizable method, providing customers extra management over their expertise. These variations affect the design of each facet of the app, from the format of components to using animations and transitions.Key concerns for UI/UX conversion embrace:
- Design Language: iOS apps adhere to Apple’s Human Interface Pointers, whereas Android apps comply with Google’s Materials Design. Materials Design emphasizes daring typography, vibrant colours, and responsive layouts.
- Navigation: iOS sometimes makes use of a tab bar or navigation bar on the prime, whereas Android typically employs a backside navigation bar or a navigation drawer.
- Gestures: iOS depends closely on swipe gestures for navigation and interactions. Android additionally helps gestures, however they’re typically built-in with the system-level navigation.
- Layouts: iOS makes use of Auto Format and Stack Views for creating responsive layouts. Android makes use of ConstraintLayout, LinearLayout, and RelativeLayout, amongst others.
- Widgets and Controls: iOS and Android have totally different units of built-in widgets and controls. Builders want to seek out the Android equivalents of iOS controls, comparable to pickers, date selectors, and alert views.
The secret’s to adapt the design to really feel native to the Android platform, even when the core performance stays the identical. A profitable conversion respects the design conventions of the goal platform.
Main Variations in APIs and Frameworks
The Utility Programming Interfaces (APIs) and frameworks present the constructing blocks for creating cell apps. iOS and Android use totally different APIs and frameworks for numerous functionalities, from accessing system {hardware} to managing person interfaces. Understanding these variations is essential for a profitable conversion.The conversion course of includes mapping iOS APIs and frameworks to their Android equivalents. This generally is a advanced activity, as some functionalities could not have a direct one-to-one mapping.
Builders typically want to seek out different options or implement customized code to attain the specified outcomes.For instance, take into account the method of accessing the system’s digicam. On iOS, you’ll sometimes use the `UIImagePickerController` or the `AVFoundation` framework. On Android, you’ll use the `Digicam` API or the `Camera2` API. Whereas each enable entry to the digicam, the implementation particulars and the way in which you deal with the info differ.This is a desk evaluating iOS and Android frameworks, itemizing their capabilities and equal Android counterparts:
| iOS Framework | Operate | Android Counterpart | Operate |
|---|---|---|---|
| UIKit | Supplies the basic constructing blocks for creating person interfaces. | Android UI (Views, Actions, Layouts) | Supplies the basic constructing blocks for creating person interfaces. |
| Core Location | Supplies location-based providers (GPS, and so on.). | Location Providers (FusedLocationProviderClient) | Supplies location-based providers (GPS, and so on.). |
| Core Knowledge | Object-graph administration and persistence. | Room Persistence Library, SQLite | Object-relational mapping (ORM) and native information storage. |
| AVFoundation | Supplies audio and video playback, recording, and enhancing capabilities. | MediaCodec, MediaPlayer, Camera2 API | Supplies audio and video playback, recording, and digicam management. |
| MapKit | Supplies map and annotation performance. | Google Maps API, Mapbox | Supplies map and annotation performance. |
This desk gives solely a glimpse of the various variations between the 2 platforms. The conversion course of calls for a radical understanding of those APIs and frameworks, together with the power to adapt and implement options which might be applicable for the goal platform.
Conversion Strategies and Approaches
So, you are seeking to port your sensible iOS app to the wild west of Android, huh? Wonderful selection! Increasing your attain to the Android ecosystem opens up an entire new world of customers and potential income. However how do you actuallydo* it? Concern not, intrepid developer! This part will break down the varied paths you possibly can take, from going native to embracing the cross-platform life, and even flirting with code translation.
We’ll discover the professionals, the cons, and the nitty-gritty particulars that will help you select the most effective route in your undertaking.
Conversion Strategies
There are a number of strategies obtainable to transform an iOS app to Android, every with its personal set of trade-offs. The selection of technique will considerably impression the event time, price, and general efficiency of the ensuing Android utility. The primary choices are native conversion, cross-platform frameworks, and code translation.
Native Conversion
Native conversion includes rewriting the iOS app’s code from scratch utilizing Android’s native languages (sometimes Java or Kotlin) and the Android SDK. This implies constructing a totally new app, tailor-made particularly for the Android platform. It is like baking an entire new cake as a substitute of simply frosting the previous one.Native conversion affords a number of benefits. The first profit is
- optimum efficiency*. Native apps can absolutely leverage the system’s {hardware} and working system options, resulting in quicker loading occasions, smoother animations, and higher general responsiveness. You get the absolute best person expertise since you’re constructing straight for the goal platform. Native growth additionally permits for
- full entry to all Android APIs and options*. That is essential in case your app depends on platform-specific functionalities, like utilizing the digicam, GPS, or different system sensors. Moreover, native growth typically gives
- larger flexibility* when it comes to design and person interface customization. You’ll be able to create a UI that completely matches the Android design pointers and person expectations. Lastly, native apps typically profit from
- higher long-term maintainability*. The code is written within the platform’s native language, making it simpler for Android builders to know, keep, and replace the app over time.
Nevertheless, native conversion additionally has its drawbacks. The largest one is the
- time and value*. Rewriting a complete app from scratch is a big endeavor, requiring a devoted crew of Android builders and a considerable funds. There’s additionally a possible for
- inconsistency between the iOS and Android variations*. Even with cautious planning, the 2 apps could have delicate variations in options, UI, or conduct. Lastly, native growth can result in
- elevated growth time*. Every characteristic must be coded, examined, and debugged individually for every platform, extending the general undertaking timeline.
Cross-Platform Frameworks
Cross-platform frameworks present a center floor, permitting builders to jot down code as soon as and deploy it on a number of platforms, together with each iOS and Android. They provide a solution to share a good portion of the codebase, decreasing growth effort in comparison with native conversion. These frameworks summary away the platform-specific particulars, offering a unified API for accessing system options and constructing person interfaces.React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin are in style examples of cross-platform frameworks.
React Native makes use of JavaScript and React to construct native-like apps. Flutter, developed by Google, makes use of the Dart language and affords a extremely performant and visually interesting UI. Xamarin, owned by Microsoft, makes use of C# and .NET to create apps that share a big portion of code throughout platforms. These frameworks intention to attenuate platform-specific code and permit builders to reuse code and assets.This is a breakdown of the professionals and cons of utilizing cross-platform frameworks for iOS to Android conversion:
- Professionals:
- Code Reusability: A good portion of the codebase could be shared between iOS and Android, decreasing growth effort and time. In some circumstances, as a lot as 70-80% of the code could be reused. This could drastically pace up the event course of.
- Quicker Improvement: Cross-platform frameworks sometimes enable for quicker growth in comparison with native conversion since you’re writing much less platform-specific code. This could result in a faster time to market.
- Value-Effectiveness: Lowering growth time and leveraging shared code can lead to decrease general growth prices. You might want fewer builders and fewer time to finish the undertaking.
- Single Codebase Administration: Sustaining a single codebase simplifies updates and bug fixes, as adjustments could be utilized to each platforms concurrently. This streamlines the upkeep course of.
- Massive Group and Ecosystem: Many cross-platform frameworks have energetic communities and intensive ecosystems with available libraries, plugins, and assets. This help community can help with problem-solving and supply entry to pre-built functionalities.
- Cons:
- Efficiency Limitations: Cross-platform apps could not at all times obtain the identical stage of efficiency as native apps, particularly when it comes to advanced animations or graphics-intensive operations. Whereas enhancements are consistently being made, there can nonetheless be a efficiency hole.
- Platform-Particular Limitations: Cross-platform frameworks could not at all times present full entry to all platform-specific options and APIs. You may want to jot down some native code to entry sure functionalities.
- UI/UX Variations: Attaining a really native feel and appear can generally be difficult, and also you may have to make compromises to keep up a constant UI throughout each platforms. Delicate UI/UX variations could come up.
- Dependency on Framework Updates: Your app’s performance and efficiency are tied to the updates and enhancements of the cross-platform framework. You may have to adapt to adjustments within the framework’s API or conduct.
- Debugging Challenges: Debugging cross-platform apps can generally be extra advanced than debugging native apps, as you are coping with each the framework and the underlying platform. Debugging instruments won’t at all times be as mature or complete.
Code Translation Instruments
Code translation instruments, also referred to as code converters or code translators, try and robotically convert code written in a single language (e.g., Goal-C or Swift) to a different language (e.g., Java or Kotlin). These instruments intention to cut back the guide effort concerned in rewriting code. They work by parsing the supply code and making an attempt to generate equal code within the goal language.Nevertheless, code translation instruments have vital limitations.
The first limitation is the
- complexity of code conversion*. Translating code from one language to a different is a posh activity, and automatic instruments typically wrestle with intricate logic, platform-specific options, and nuanced coding types. The
- high quality of the generated code* generally is a concern. Translated code might not be as environment friendly, readable, or maintainable as code written by a human developer. Moreover, code translation instruments
- could not help all options* of the unique code. Platform-specific APIs, UI components, and libraries won’t be absolutely convertible, requiring guide changes. Lastly, code translation instruments could be
troublesome to keep up*. The generated code may be arduous to know and debug, making it difficult to make adjustments or repair bugs. Contemplate a situation
a posh monetary app constructed with intricate algorithms and particular iOS UI components is run by a code translation instrument. The instrument may efficiently convert the fundamental logic, however it’s prone to wrestle with the UI, resulting in a clunky person expertise on Android. The translated code may also have efficiency points, making the app sluggish and unresponsive.
Native Conversion
Alright, let’s roll up our sleeves and dive headfirst into the world of native app conversion. This is not only a easy copy-paste state of affairs; we’re speaking a couple of full rewrite, a contemporary begin, an opportunity to construct one thing wonderful from the bottom up, tailor-made particularly for the Android ecosystem. Consider it as a meticulously deliberate journey, a fastidiously constructed bridge between two distinct technological landscapes.
Rewriting iOS Apps for Android in Java or Kotlin
Changing an iOS app to Android utilizing the native method includes an entire code overhaul, translating the app’s performance from Swift or Goal-C to both Java or Kotlin. This course of calls for a stable understanding of each iOS and Android growth paradigms, together with their respective UI frameworks, APIs, and platform-specific options. It is like studying a brand new language – you could grasp the grammar, the vocabulary, and the nuances to successfully talk.This is a breakdown of the everyday steps concerned:
- Planning and Evaluation: Earlier than you even contact the code, meticulously analyze the present iOS app. Perceive its structure, options, and dependencies. Doc every little thing! This part includes creating an in depth blueprint for the Android model, together with UI design, characteristic parity, and target market.
- Selecting Your Weapon: Choose your programming language. Java, the standard workhorse, affords stability and an enormous ecosystem. Kotlin, the fashionable, concise, and interoperable possibility, is formally supported by Google and sometimes favored for its class and security options. Your selection will affect your coding type and the libraries you utilize.
- Setting Up the Android Mission: Create a brand new Android undertaking in Android Studio, the official IDE. Configure the undertaking settings, together with the goal SDK, construct instruments, and dependencies. This step is akin to getting ready your canvas earlier than you begin portray.
- UI Recreation: Rebuild the person interface utilizing Android’s UI elements (Views, Layouts, Actions, Fragments). Translate the iOS app’s design components into their Android equivalents. This may contain adapting UI components like buttons, textual content fields, and tables to match the Android feel and appear.
- Logic and Performance Translation: Rewrite the app’s core logic and performance. That is the place you translate Swift or Goal-C code into Java or Kotlin. This consists of dealing with person enter, information processing, and interactions with the system’s {hardware}.
- Testing and Debugging: Rigorously check the Android app on numerous units and emulators. Determine and repair bugs, optimize efficiency, and guarantee a easy person expertise. That is the essential high quality assurance part.
- Deployment: Put together the app for launch on the Google Play Retailer. This consists of making a launch construct, producing signing keys, and offering all the required metadata and property.
Migrating UI Parts and Performance
The migration of UI components and performance is a crucial facet of native conversion. You might be basically recreating the visible and interactive features of your iOS app utilizing Android’s native UI elements and APIs. This course of calls for cautious consideration to element to make sure that the person expertise on Android mirrors the performance and intuitiveness of the iOS model, even when the underlying expertise is totally different.Right here’s a deeper look:
- UI Factor Mapping: iOS UI components like `UIButton`, `UILabel`, and `UITextField` have direct equivalents in Android, comparable to `Button`, `TextView`, and `EditText`. The problem lies in understanding the delicate variations of their conduct, properties, and styling choices. For instance, iOS makes use of `Auto Format` for UI association, whereas Android makes use of `ConstraintLayout` (or older format managers like `LinearLayout` or `RelativeLayout`).
- Format Administration: iOS makes use of storyboards and XIB recordsdata for UI design. Android makes use of XML layouts and, more and more, declarative UI with Jetpack Compose. You have to to translate the format construction and ingredient positioning from iOS to Android utilizing the suitable format managers. Think about using instruments like Android Studio’s format editor to visually design your layouts.
- Occasion Dealing with: iOS makes use of `target-action` patterns and delegates for occasion dealing with. Android makes use of `OnClickListener` interfaces and different occasion listeners. You may have to rewrite the occasion dealing with logic to adapt to Android’s occasion mannequin.
- Knowledge Binding: In case your iOS app makes use of information binding (e.g., utilizing bindings in Swift or Goal-C), you will have to implement an identical mechanism in Android. Android gives information binding libraries that simplify this course of.
- Animations and Transitions: iOS has strong animation capabilities. Android additionally gives highly effective animation frameworks. You may have to recreate the animations and transitions within the Android app, doubtlessly utilizing Android’s animation APIs or third-party libraries.
Dealing with Platform-Particular Options
Platform-specific options require particular consideration throughout conversion, as they typically contain utilizing totally different APIs and SDKs. Push notifications, in-app purchases, and entry to system {hardware} are prime examples. The secret’s to leverage the native Android APIs to duplicate the performance supplied by the iOS counterparts.This is learn how to sort out some widespread platform-specific options:
- Push Notifications: In iOS, you utilize Apple Push Notification Service (APNs). In Android, you utilize Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM). The implementation includes integrating the FCM SDK, dealing with system registration, and managing the sending and receiving of push notifications. You may have to rewrite the notification registration and dealing with logic to make use of FCM’s APIs.
- In-App Purchases: iOS makes use of StoreKit for in-app purchases. Android makes use of Google Play Billing. You may have to combine the Google Play Billing Library, deal with buy flows, handle product subscriptions, and confirm purchases on the server-side.
- Machine {Hardware} Entry: Accessing system options just like the digicam, GPS, and sensors requires utilizing the suitable Android APIs (e.g., `Digicam`, `LocationManager`, `SensorManager`). You may have to request the required permissions from the person and deal with the info accordingly. Bear in mind to test for system compatibility and deal with potential errors.
- Platform-Particular Libraries: In case your iOS app makes use of any platform-specific libraries or SDKs, you will want to seek out equal Android libraries or alternate options. Analysis and select the suitable Android libraries to attain the specified performance.
Changing iOS Code Snippets to Android
Let’s take into account a sensible instance: changing a community request from Swift to Java/Kotlin.In Swift (iOS):“`swiftimport Foundationfunc fetchData(from url: URL, completion: @escaping (Consequence ) -> Void) let activity = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url) (information, response, error) in if let error = error completion(.failure(error)) return guard let information = information else completion(.failure(NSError(area: “DataError”, code: 0, userInfo: nil))) return completion(.success(information)) activity.resume()“`This Swift code makes use of `URLSession` to fetch information from a given URL. The completion handler receives both the info or an error.Now, let’s translate this to Kotlin (Android):“`kotlinimport java.io.IOExceptionimport kotlinx.coroutines.Dispatchersimport kotlinx.coroutines.withContextimport java.web.URLimport java.web.HttpURLConnectionsuspend enjoyable fetchData(url: String): Consequence return withContext(Dispatchers.IO) attempt val urlConnection = URL(url).openConnection() as HttpURLConnection attempt val inputStream = urlConnection.inputStream val byteArray = inputStream.readBytes() Consequence.success(byteArray) catch (e: IOException) Consequence.failure(e) lastly urlConnection.disconnect() catch (e: Exception) Consequence.failure(e) “`This Kotlin code makes use of `HttpURLConnection` to carry out a community request. The `fetchData` operate is a suspending operate, designed to be known as from a coroutine. It makes use of `Dispatchers.IO` to carry out the community operation on a background thread, stopping blocking the principle thread and guaranteeing a responsive person expertise. The operate returns a `Consequence` object, indicating success or failure.
Code Instance: Changing a Widespread iOS Operate to Its Android Equal
This is a code instance illustrating the conversion of a standard iOS operate to its Android equal, together with feedback to elucidate the adjustments.iOS (Swift):“`swift// iOS: Operate to format a dateimport Foundationfunc formatDate(date: Date, format: String) -> String let dateFormatter = DateFormatter() dateFormatter.dateFormat = format return dateFormatter.string(from: date)// Instance usagelet currentDate = Date()let formattedDate = formatDate(date: currentDate, format: “MM/dd/yyyy”)print(formattedDate) // Output: 03/08/2024 (Instance)“`Android (Kotlin):“`kotlin// Android: Operate to format a dateimport java.textual content.SimpleDateFormatimport java.util.Dateimport java.util.Localefun formatDate(date: Date, format: String): String // Create a SimpleDateFormat object with the required format and locale.
val dateFormatter = SimpleDateFormat(format, Locale.getDefault()) // Format the date utilizing the SimpleDateFormat. return dateFormatter.format(date)// Instance usageval currentDate = Date()val formattedDate = formatDate(currentDate, “MM/dd/yyyy”)println(formattedDate) // Output: 03/08/2024 (Instance)“`
The iOS Swift code makes use of `DateFormatter` to format dates. The Android Kotlin code makes use of `SimpleDateFormat`, which is the equal class. Each use a format string to specify the specified date and time format. The instance reveals learn how to format a date to “MM/dd/yyyy” in each platforms. The Kotlin code consists of the `Locale.getDefault()` to deal with the totally different areas.
Cross-Platform Frameworks
So, you are seeking to take your shiny iOS app and get it enjoying good with the Android crowd? Wonderful! That is the place cross-platform frameworks strut their stuff. They promise a single codebase that magically transforms into apps for each platforms. Appears like a developer’s dream, proper? Effectively, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of those frameworks, weighing the great, the unhealthy, and the marginally much less fairly features of every.
Evaluating React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin
Let’s get all the way down to brass tacks and examine three of the large gamers within the cross-platform recreation: React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin. Every has its personal strengths and weaknesses in relation to changing an iOS app to Android.
- React Native: Constructed on JavaScript and React, React Native permits you to construct native-looking apps utilizing acquainted net applied sciences. It is obtained an enormous neighborhood and an enormous library of pre-built elements, making growth comparatively quick.
- Flutter: Google’s Flutter makes use of the Dart programming language and renders UI straight, resulting in spectacular efficiency and a constant feel and appear throughout platforms. It is obtained a rising neighborhood and a deal with stunning, customizable UIs.
- Xamarin: Owned by Microsoft, Xamarin makes use of C# and .NET to create native apps. It affords sturdy platform-specific options and glorious integration with the .NET ecosystem.
Benefits of Utilizing a Cross-Platform Framework
The attract of cross-platform growth is powerful. The benefits could be compelling, particularly when assets are tight or time is of the essence.
- Code Reusability: That is the large one. Write your code as soon as, and deploy it on each iOS and Android. This dramatically reduces growth effort and time. Think about solely having to debug a single codebase!
- Quicker Improvement: With a shared codebase, you are basically constructing two apps directly. This could result in considerably quicker time-to-market.
- Value-Effectiveness: Hiring a single crew to develop and keep a cross-platform app could be cheaper than hiring separate groups for iOS and Android. That is significantly interesting for startups and small companies.
- Simplified Upkeep: Updates and bug fixes are utilized to a single codebase, making upkeep simpler and extra environment friendly.
Disadvantages of Utilizing a Cross-Platform Framework
Whereas cross-platform frameworks supply many advantages, they are not a silver bullet. There are potential drawbacks to contemplate.
- Efficiency Limitations: Whereas efficiency has improved considerably, cross-platform apps can generally lag behind native apps when it comes to pace and responsiveness. That is very true for advanced apps with demanding options.
- Platform-Particular Challenges: Accessing sure native options and APIs could be tough, requiring workarounds or platform-specific code. This could add complexity to the event course of.
- UI Limitations: Attaining pixel-perfect UI parity throughout each platforms could be difficult. You may have to make compromises to make sure a constant person expertise.
- Dependency on Framework Updates: Your app’s performance and efficiency are tied to the framework’s updates. If the framework lags behind in supporting new options or bug fixes, your app might endure.
Choosing the Finest Cross-Platform Framework
Selecting the best framework relies upon closely in your particular app and your crew’s experience. Contemplate these elements:
- App Complexity: For easy apps, any framework may work properly. For advanced apps with demanding options, Flutter or Xamarin may be higher decisions attributable to their efficiency capabilities.
- Efficiency Necessities: In case your app requires top-notch efficiency, native growth or a framework like Flutter may be most well-liked.
- Workforce Experience: Select a framework that your crew is snug with and has expertise in. Studying a brand new language or framework takes effort and time.
- Group Assist: A big and energetic neighborhood gives entry to useful assets, libraries, and options to widespread issues. React Native has an enormous neighborhood, whereas Flutter’s is quickly rising.
- Platform-Particular Options: In case your app depends closely on platform-specific options, take into account a framework like Xamarin that provides sturdy native integration.
Framework Comparability Desk
This is a desk evaluating React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin that will help you visualize their strengths and weaknesses in relation to iOS to Android conversion:
| Framework | Strengths | Weaknesses | Conversion Issues | Group Assist |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| React Native | Massive neighborhood, quick growth, makes use of JavaScript/React, intensive libraries. | Efficiency generally is a concern, potential for UI inconsistencies, JavaScript can introduce runtime errors. | Simpler to reuse current net growth abilities, good for easy to medium complexity apps. | Extraordinarily giant and energetic. |
| Flutter | Wonderful efficiency, stunning UI, constant feel and appear, quick growth, rising neighborhood. | Dart language (studying curve), smaller neighborhood than React Native, restricted native library help initially. | Wonderful for UI-intensive apps, gives glorious efficiency, and quickly rising help. | Rising quickly, with rising assets and help. |
| Xamarin | Native efficiency, sturdy platform integration, makes use of C# and .NET, good for advanced apps. | Steeper studying curve (C#), could be extra advanced to arrange, requires .NET experience. | Wonderful for apps needing native options, requires .NET growth data, affords entry to platform-specific APIs. | Good, backed by Microsoft, and well-documented. |
UI/UX Issues for Android
So, you are porting your shiny iOS app over to the land of Android? Superior! However maintain your horses – it isn’t only a easy copy-paste state of affairs. Android and iOS, whereas each serving the identical aim of offering an excellent person expertise, communicate totally different visible languages. Ignoring these nuances will result in an app that seems like a stranger in a well-recognized land.
Let’s dive into learn how to make your app really feel proper at residence on Android.
Adapting to Android’s Design Pointers (Materials Design)
Android’s visible type is basically dictated by Materials Design, a design language developed by Google. It emphasizes clear layouts, intuitive interactions, and a deal with realism by using shadows, depth, and animation. Consider it because the creative blueprint for a way an Android appshould* feel and appear. Adhering to those pointers is essential for creating an app that feels native and pure to Android customers.
This may result in elevated person satisfaction and a greater general expertise.
- Key Ideas: Materials Design is constructed on a number of core rules:
- Materials: The visible metaphor relies on the concept of bodily surfaces and supplies, comparable to paper and ink. This permits for practical results like shadows and depth.
- Daring, Graphic, Intentional: Materials Design makes use of sturdy visible cues, like shade and typography, to information customers by the app and spotlight key info.
- Movement Supplies Which means: Animations and transitions aren’t only for present; they serve to make clear interactions and supply suggestions to the person.
- Adaptive: Materials Design permits your app to adapt and reply to numerous display screen sizes and system capabilities.
- Shade and Typography: Materials Design gives a complete shade palette and pointers for typography. It is really useful to make use of the supplied shade palettes or create a customized palette that adheres to Materials Design rules. For typography, keep on with fonts really useful by Materials Design.
- Elements: Materials Design affords an enormous library of pre-built UI elements (buttons, playing cards, lists, and so on.). Using these elements ensures consistency with different Android apps and reduces growth time.
- Sources: The official Materials Design pointers ([https://material.io/](https://materials.io/)) are your greatest buddy. They provide detailed info, element specs, and design assets.
Navigation Patterns on Android
iOS and Android method navigation otherwise, and it is important to know these variations. iOS apps typically depend on a hierarchical navigation mannequin, utilizing a again button on the prime left to navigate up the stack. Android, alternatively, makes use of a extra versatile method, together with the again button (often a system button), the navigation drawer, and backside navigation. Ignoring these variations will make your app really feel clunky and unintuitive.
- Again Button: The again button is an important a part of the Android expertise. It permits customers to retrace their steps and return to the earlier display screen. It is essential to make sure that the again button capabilities accurately in your ported app.
- Navigation Drawer: The navigation drawer (a slide-out menu sometimes accessed by swiping from the left fringe of the display screen) is a standard sample for displaying app navigation choices. It’s helpful for accessing totally different sections of your app rapidly.
- Backside Navigation: Backside navigation is right for apps with a small variety of top-level locations. It gives fast entry to core sections of your app and is straightforward to make use of with one hand.
- Tabs: Tabs are one other navigation sample used to prepare content material inside a display screen. They are often positioned on the prime or backside of the display screen.
- Issues:
- Hierarchy: Android apps typically have a flatter hierarchy than iOS apps. Take into consideration learn how to set up your app’s content material to attenuate the variety of steps required to achieve any specific characteristic.
- Contextual Actions: Android apps continuously use contextual motion bars (toolbars that seem on the prime of the display screen) to supply actions related to the present display screen.
Creating Responsive Layouts for Android
Android units are available in all sizes and styles, from small telephones to giant tablets. Your app must adapt seamlessly to all of them. Responsive design is the important thing. This includes creating layouts that alter robotically to totally different display screen sizes and resolutions, guaranteeing that your app appears good and capabilities accurately on each system.
- Format Managers: Android gives numerous format managers that will help you construction your UI:
- LinearLayout: Organizes views in a single row or column.
- RelativeLayout: Positions views relative to one another.
- ConstraintLayout: A strong format supervisor that enables for advanced layouts with versatile constraints. That is typically really useful.
- Models of Measurement:
- dp (Density-independent pixels): The really useful unit for specifying UI ingredient sizes. It adjusts robotically based mostly on the display screen density.
- sp (Scale-independent pixels): Used for textual content sizes, and it additionally adjusts based mostly on person’s most well-liked font dimension within the system settings.
- Supporting Totally different Display Sizes:
- Use ConstraintLayout: That is typically the popular method as it’s the most versatile and handles the totally different sizes very properly.
- Create different layouts: For very totally different display screen sizes (e.g., tablets), you may have to create totally different format recordsdata. Android lets you specify format recordsdata based mostly on display screen dimension, orientation, and different elements.
- Adaptive UI: Design your UI components to scale and alter their positions based mostly on display screen dimension.
- Display Density: Android units have various display screen densities (low, medium, excessive, extra-high, and so on.). To make sure your app appears crisp on all units, present totally different variations of your photos for various densities. Android will robotically choose the suitable picture based mostly on the system’s display screen density.
- Testing: Check your app on a wide range of units and display screen sizes to make sure it is responsive and appears appropriate. Android Studio’s emulator and numerous on-line system emulators are your greatest pals.
Widespread UI Parts to Redesign or Exchange, Convert ios app to android
Sure UI components are dealt with otherwise on iOS and Android. You may have to adapt these to the Android platform to supply a local really feel. This could typically be essentially the most time-consuming facet of the conversion course of, however the payoff is a significantly better person expertise.
- Buttons: iOS makes use of rounded-corner buttons with a delicate shadow impact. Android’s Materials Design emphasizes flat, rectangular buttons with a ripple impact on contact.
- Navigation Bars: iOS navigation bars sometimes have a title, a again button, and sometimes a number of different motion buttons. Android makes use of a toolbar (a part of the app’s format) for comparable performance, typically incorporating a menu icon or a search icon.
- Tab Bars: iOS tab bars are sometimes situated on the backside of the display screen. Android affords each backside navigation (Materials Design) and prime tabs.
- Pickers (Date/Time): iOS has its personal date/time pickers. Android gives its personal Materials Design-compliant date and time pickers.
- Alerts/Dialogs: iOS makes use of a definite type for alerts. Android gives dialogs that adhere to Materials Design.
- Lists and Tables: Each platforms have record and desk views, however the visible styling and interplay are totally different. It would be best to use the suitable Android elements.
Illustration:Think about a side-by-side comparability. On the left, we see a screenshot of an iOS app. The highest navigation bar is glossy, with a transparent title centered, a again button within the prime left, and probably some motion buttons on the appropriate. Buttons are rounded rectangles with a slight gradient and a shadow. The colour palette is probably going influenced by the app’s model, however it’s typically clear and minimal.Now, take a look at the Android model on the appropriate.
The highest space is a toolbar, which appears extra like a body with a title, a menu icon (three horizontal strains), and maybe a search icon. The again button is represented by a left-pointing arrow, which is a part of the system UI. The buttons are flat rectangles with delicate animations on contact, adhering to Materials Design rules. The colours are extra vibrant and daring, with a deal with main and accent colours that spotlight key interactions.
The spacing is barely extra beneficiant, and the general look is cleaner and extra purposeful. The underside navigation bar, if current, options icons with labels which might be clear and straightforward to faucet. The visible language is all about depth, with shadows and delicate animations offering visible suggestions. This comparability showcases the basic variations in visible language and person expertise between the 2 platforms.
The iOS model emphasizes a extra minimalist method, whereas the Android model embraces Materials Design’s emphasis on visible hierarchy, daring colours, and interactive components.
Testing and Debugging

So, you have taken the plunge and transformed your iOS app to Android. Congratulations! However the journey is not over simply but. Now comes the essential part: guaranteeing your app works flawlessly on its new platform. Consider it like this: you would not simply construct a home after which hope the roof does not leak, proper? Testing and debugging are your important instruments for a easy transition, guaranteeing your customers have a top-notch expertise.
Let’s dive into how to ensure your Android app shines.
Testing Procedures for Purposeful Accuracy
Thorough testing is the cornerstone of a profitable Android app conversion. It is not nearly seeing if the appruns*; it is about guaranteeing each characteristic, each button, each interplay behaves as anticipated. Contemplate this a complete high quality assurance guidelines.
- Unit Testing: This includes testing particular person elements or capabilities of your app in isolation. Consider it as checking every brick in your home earlier than constructing the wall. For instance, if in case you have a operate that calculates the full price of things in a procuring cart, you’d write unit assessments to confirm it really works accurately with totally different numbers of things and costs.
This helps to pinpoint the precise location of errors, comparable to within the formulation, and makes it simpler to repair them.
- Integration Testing: As soon as the person elements are verified, integration testing checks how they work collectively. It is like checking how the partitions, doorways, and home windows match collectively to kind the whole construction. For instance, you’d check how the login characteristic integrates with the person profile characteristic or how the fee gateway integrates with the procuring cart characteristic.
- System Testing: That is the excellent check of the whole system, checking the app as an entire. It includes testing all functionalities and options of the app to make sure they work accurately collectively. For instance, the app’s general efficiency, together with its responsiveness, useful resource utilization, and stability, needs to be completely examined below totally different eventualities, comparable to various community circumstances and person hundreds.
- Person Acceptance Testing (UAT): This includes having actual customers check the app to make sure it meets their wants and expectations. It is like having potential householders stroll by your accomplished home to supply suggestions. Beta testing, the place a gaggle of customers assessments the app earlier than its public launch, falls below this class. Person suggestions is invaluable for figuring out usability points and guaranteeing the app delivers a constructive person expertise.
- Efficiency Testing: This measures the app’s pace, stability, and useful resource utilization below totally different circumstances. This consists of testing for reminiscence leaks, CPU utilization, and battery consumption.
- Safety Testing: That is essential to establish and handle any vulnerabilities that would compromise person information or app performance. This could embrace penetration testing, the place testers simulate assaults to seek out weaknesses, or static evaluation, the place the code is reviewed for potential safety flaws.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensures the app works accurately throughout a variety of Android units, display screen sizes, and working system variations. That is crucial as a result of Android units differ considerably.
Emulators and Bodily Gadgets for App Testing
The selection between emulators and bodily units is essential for efficient testing. Every affords distinct benefits and downsides.
- Emulators: Emulators are software program packages that simulate Android units in your pc. They’re extremely handy for preliminary testing as a result of you possibly can rapidly check on totally different display screen sizes and Android variations with out proudly owning a number of units. The Android SDK (Software program Improvement Package) gives a built-in emulator.
- Bodily Gadgets: Nothing beats testing on an actual system. Bodily units present essentially the most correct illustration of how your app will carry out in the true world. They account for device-specific {hardware} variations and efficiency traits that emulators cannot absolutely replicate. Testing on bodily units is important to establish device-specific points, comparable to these associated to sensors (GPS, digicam), and to optimize efficiency for various {hardware} configurations.
Contemplate this comparability:
| Characteristic | Emulator | Bodily Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Value | Free (included with Android SDK) | Requires buying units |
| Comfort | Excessive (straightforward to change between units) | Decrease (requires connecting and disconnecting units) |
| Efficiency | Will be sluggish, particularly with advanced apps | Extra correct efficiency illustration |
| Accuracy | Simulates system, however not completely | Most correct illustration of real-world use |
| Debugging | Debugging instruments obtainable inside the emulator | Extra strong debugging instruments, entry to system logs |
Widespread Debugging Strategies and Instruments
Debugging is the artwork of discovering and fixing bugs. It is an important ability for any Android developer. Listed here are some widespread strategies and instruments that will help you in your quest to eradicate these pesky errors.
- Logcat: Logcat is Android’s built-in logging system. It lets you print messages out of your app to the console. It is your main supply of data when one thing goes mistaken. Use `Log.d()`, `Log.e()`, `Log.w()`, and so on., to log several types of messages (debug, error, warning). For instance:
Log.e(“MyActivity”, “Error: One thing went mistaken!”);
This may print an error message to the console with the tag “MyActivity.”
- Android Studio Debugger: Android Studio comes with a strong debugger that allows you to step by your code line by line, examine variables, set breakpoints, and study the decision stack. That is like having a magnifying glass to look at each element of your app’s execution.
- Breakpoints: Breakpoints are markers you set in your code that pause execution at a particular line. This allows you to examine the state of your app at that time.
- Watch Variables: Add variables to the “Watch” window within the debugger to watch their values as your app runs. This helps you observe adjustments and establish surprising values.
- Exception Dealing with: Use `try-catch` blocks to deal with exceptions gracefully. This prevents your app from crashing and gives you with details about what went mistaken.
- Lint: Android Lint is a code evaluation instrument that checks your code for potential issues, comparable to efficiency points, safety vulnerabilities, and stylistic errors. It is like having a grammar checker in your code.
- Reminiscence Profiler: The Reminiscence Profiler in Android Studio helps you establish reminiscence leaks and optimize your app’s reminiscence utilization.
- Community Profiler: The Community Profiler helps you monitor your app’s community exercise, together with HTTP requests and responses. That is useful for diagnosing network-related points.
Addressing Platform-Particular Points Throughout Testing
Changing from iOS to Android typically means coping with platform-specific quirks. Listed here are some ideas for tackling these challenges.
- UI Variations: Android’s UI (Person Interface) is totally different from iOS. Guarantee your transformed UI appears and capabilities accurately on Android units. This may contain adjusting layouts, utilizing totally different UI components, and adapting to Android’s design pointers. As an example, the position of the “again” button (sometimes on the prime left on iOS) differs from Android.
- Permissions: Android has a distinct permission mannequin than iOS. Make sure you request and deal with permissions accurately. For instance, you will have to request permission to entry the digicam, location, or contacts.
- Display Sizes and Densities: Android units are available in numerous display screen sizes and densities. Check your app on a number of units to make sure it appears good on all of them. Use format recordsdata and useful resource qualifiers to adapt your UI to totally different display screen sizes.
- Android Variations: Android has many variations, every with its personal options and quirks. Check your app on a number of Android variations to make sure compatibility. Contemplate the goal SDK model and the minimal SDK model in your app.
- {Hardware} Variations: Android units differ in {hardware}, comparable to cameras, sensors, and processors. Check your app on totally different units to make sure it really works accurately with totally different {hardware}.
- Libraries and Dependencies: Be sure that any third-party libraries or dependencies you utilize are appropriate with Android. If crucial, discover Android-specific alternate options.
- Notifications: Implement Android-specific notification options and guarantee they operate accurately.
Efficiency Optimization
So, you have efficiently navigated the treacherous waters of iOS to Android app conversion. Congratulations! However the journey does not finish there. Now, it is time to guarantee your newly minted Android app runs like a finely tuned machine, not a clunky jalopy. Efficiency optimization is essential for person satisfaction and app success. A sluggish app will rapidly discover itself gathering mud within the huge app retailer panorama.
Let’s dive into the methods to maintain your app zipping alongside.
Methods for Optimizing Transformed Android App Efficiency
Optimizing the efficiency of your transformed Android app requires a multi-faceted method. It includes scrutinizing each facet of the app’s operation, from the code itself to the way it interacts with the system’s assets. Contemplate these methods as your toolbox for attaining peak efficiency.
- Code Profiling: Use Android Studio’s profiler to establish efficiency bottlenecks. This instrument lets you analyze CPU utilization, reminiscence allocation, community exercise, and extra. Pinpointing these areas is step one towards optimization. Think about it as a physician diagnosing a affected person’s illnesses earlier than prescribing therapy.
- Cut back UI Overdraw: Overdraw happens when the identical pixel is drawn a number of occasions in a single body. This wastes invaluable processing energy and results in a sluggish UI. Instruments just like the “Present GPU Overdraw” possibility in Developer Choices on Android may also help visualize overdraw. Purpose for minimal overdraw – consider it as minimizing pointless brushstrokes in a portray.
- Optimize Picture Loading: Massive photos can considerably impression efficiency. Use libraries like Glide or Picasso to effectively load and cache photos. These libraries deal with picture resizing, caching, and different optimizations robotically. Consider it as utilizing a high-efficiency engine in your image-loading duties.
- Environment friendly Knowledge Dealing with: Reduce community requests and optimize information parsing. Cache information at any time when doable to cut back the necessity to fetch it repeatedly. Think about using a database like Room for native information storage. That is like streamlining your provide chain, guaranteeing fast entry to the assets your app wants.
- Background Activity Administration: Keep away from performing long-running duties on the principle thread, as this could freeze the UI. Use background threads or providers for duties like community requests or information processing. Consider it as assigning duties to totally different departments inside an organization to forestall bottlenecks.
- Code Minification and Obfuscation: These strategies cut back the scale of your app and make it more durable to reverse engineer. ProGuard (or R8) can be utilized to minify, optimize, and obfuscate your code. That is like shrinking your baggage earlier than a visit to make it lighter and extra manageable.
Figuring out and Addressing Widespread Efficiency Bottlenecks in Android Apps
Each app, particularly one which’s been by a conversion, faces potential efficiency pitfalls. Recognizing these widespread bottlenecks is vital to stopping them from hindering your app’s efficiency. Let’s take a look at the same old suspects and learn how to deal with them.
- Gradual UI Rendering: This may be attributable to advanced layouts, extreme UI updates, or operations on the principle thread. Optimize layouts by utilizing ConstraintLayout, which permits for extra environment friendly UI rendering. Reduce UI updates and transfer long-running operations to background threads.
- Reminiscence Leaks: Reminiscence leaks happen when objects are not wanted however are nonetheless held in reminiscence, resulting in elevated reminiscence utilization and potential crashes. Use instruments like LeakCanary to detect reminiscence leaks. Be sure that assets (e.g., bitmaps, database connections) are correctly launched when not wanted.
- Extreme Community Requests: Too many community requests can drain battery and decelerate the app. Implement caching mechanisms to cut back the variety of requests. Batch requests when doable and use environment friendly information codecs like JSON.
- Inefficient Database Operations: Gradual database queries can impression efficiency. Optimize your database schema, use indexes, and keep away from advanced queries that may take a very long time to execute. Think about using asynchronous database operations to keep away from blocking the UI thread.
- Battery Drain: Inefficient code can result in extreme battery drain, which might frustrate customers. Optimize community requests, decrease using background providers, and use battery-efficient picture loading strategies.
Significance of Code Optimization and Environment friendly Useful resource Administration
Code optimization and environment friendly useful resource administration are the cornerstones of a high-performing Android app. They straight impression person expertise and the app’s general success. Consider it as the muse upon which your app’s home is constructed.
Code Optimization:
Clear, environment friendly code is the important thing. Effectively-written code executes quicker, consumes much less reminiscence, and is less complicated to keep up. This interprets to a smoother, extra responsive person expertise. It includes eliminating pointless code, streamlining algorithms, and selecting essentially the most environment friendly information buildings. For instance, changing a nested loop with a extra environment friendly algorithm can dramatically enhance efficiency, particularly when coping with giant datasets.
A well-optimized code is sort of a well-oiled machine, working seamlessly and effectively.
Environment friendly Useful resource Administration:
Android units have restricted assets (CPU, reminiscence, battery). Environment friendly useful resource administration ensures that your app makes use of these assets properly. This consists of:
- Releasing assets when they’re not wanted (e.g., closing database connections, releasing bitmap assets).
- Utilizing the suitable information buildings and algorithms to attenuate reminiscence utilization.
- Minimizing community requests and information transfers to preserve battery.
Environment friendly useful resource administration prevents your app from hogging system assets, guaranteeing it coexists peacefully with different apps and delivers a constructive person expertise. Consider it as being an excellent neighbor, respecting the shared assets and contributing to a harmonious atmosphere.
Suggestions for Enhancing App Loading Instances, Responsiveness, and Battery Utilization
High-quality-tuning your app to excel in loading occasions, responsiveness, and battery utilization is a continuing pursuit. Listed here are particular suggestions, actionable steps to show principle into observe.
- Optimize App Loading Instances:
- Cut back Startup Duties: Defer non-essential duties till after the app has began.
- Use Splash Screens Successfully: Show a splash display screen whereas the app hundreds, however preserve it temporary and informative.
- Lazy Load Sources: Load assets solely when they’re wanted.
- Improve Responsiveness:
- Use Asynchronous Operations: Carry out long-running duties (community requests, database operations) on background threads to forestall UI freezes.
- Optimize UI Rendering: Use environment friendly format buildings (e.g., ConstraintLayout) and decrease overdraw.
- Implement Contact Occasion Dealing with Effectively: Reply to person interactions promptly.
- Enhance Battery Utilization:
- Optimize Community Requests: Batch requests, use environment friendly information codecs, and decrease the frequency of requests.
- Handle Background Providers: Use background providers sparingly and schedule them effectively.
- Optimize Picture Loading: Use environment friendly picture loading libraries (e.g., Glide, Picasso) and compress photos.
- Use Wake Locks Correctly: Solely use wake locks when completely crucial and launch them promptly.
Instance: Contemplate an e-commerce app. A person clicks on a product picture. If the picture is giant and never optimized, the app could freeze whereas it hundreds. Through the use of a library like Glide to effectively load and cache the picture, the app stays responsive, and the person enjoys a seamless expertise. Moreover, deferring the loading of product suggestions till after the principle product particulars are displayed permits for a quicker preliminary load time.
